SEER to SEER2 Conversion: Understanding the 2025 Air Conditioner Efficiency Standard
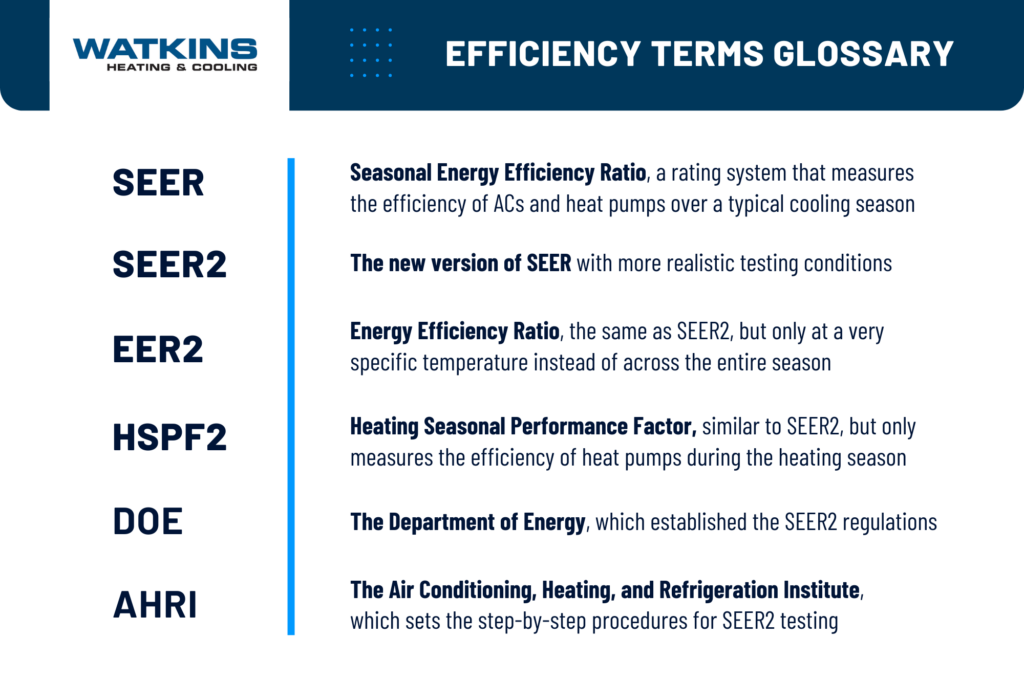
What is SEER?
What on Earth is SEER2, how is it different than the regular old SEER rating, and what does it mean for my cooling and heating system?
The recent move to the SEER2 rating for air conditioning systems has left a lot of people scratching their heads wondering what this means, so we’re here to clear the air for you!
Let’s start by explaining what a SEER rating is for those who may not know. SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio and is a rating system that tells us the cooling efficiency of air conditioning units and heat pumps. The higher the number, the more energy efficient the system is.
The US Department of Energy (DOE) developed the SEER testing standard to ensure all HVAC manufacturers measure air conditioning efficiency the same way. While the DOE sets the regulations for this testing, the exact steps in the procedure are developed by the AHRI (Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute). They also determine the controlled environment in the laboratory including temperature, humidity, and time range, to simulate the average outdoor cooling conditions in the United States.
The great part about this rating system is that every air conditioner and heat pump is assigned a SEER number. So homeowners shopping for a new HVAC system can use that one standard number to do an apples to apples comparison of several different AC units.
Now that you understand what SEER is, let’s get into how SEER2 came about!
What is SEER2?
SEER2 is the next generation of AC efficiency ratings, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
In 2016, the Department of Energy altered their original SEER testing standards for air conditioners to include a new “M1” blower testing procedure. M1 is a broad term referring to the DOE’s new and improved efficiency regulations.
This change in testing led to a change in name from SEER to SEER2 and a requirement that all manufacturers re-test their split system air conditioners and heat pumps by January 1, 2023.
Just like the old SEER measurement, SEER2 tells us the efficiency of your cooling system, but based on more realistic testing conditions than before. The new SEER2 standards better account for factors like how long the system runs, required maintenance, and ductwork. For instance, the external static pressure was increased from 0.1” w.g. to 0.5”, to test an AC as if it’s connected to an actual duct system rather than just on a lab bench.
The DOE’s long-term goal here is to reduce energy consumption. Their new regulations help move the HVAC industry toward a more sustainable future, and their research predicts US. homes using SEER2 systems to save $3 billion – $12 billion on their energy bills over the next 30 years.
The unfortunate short-term effect of the move has been confusion among homeowners. Models manufactured before 2023 still have the old SEER rating while those made in 2023 and beyond are rated SEER2 and have new corresponding model numbers. Hopefully, after the existing inventory is out of the supply chain, we can all forget the old SEER rating was ever a thing and move on!
How to Convert SEER to SEER2
In 2025, all new air conditioning and heat pump systems you see will have the new SEER2 rating rather than the the old SEER rating.
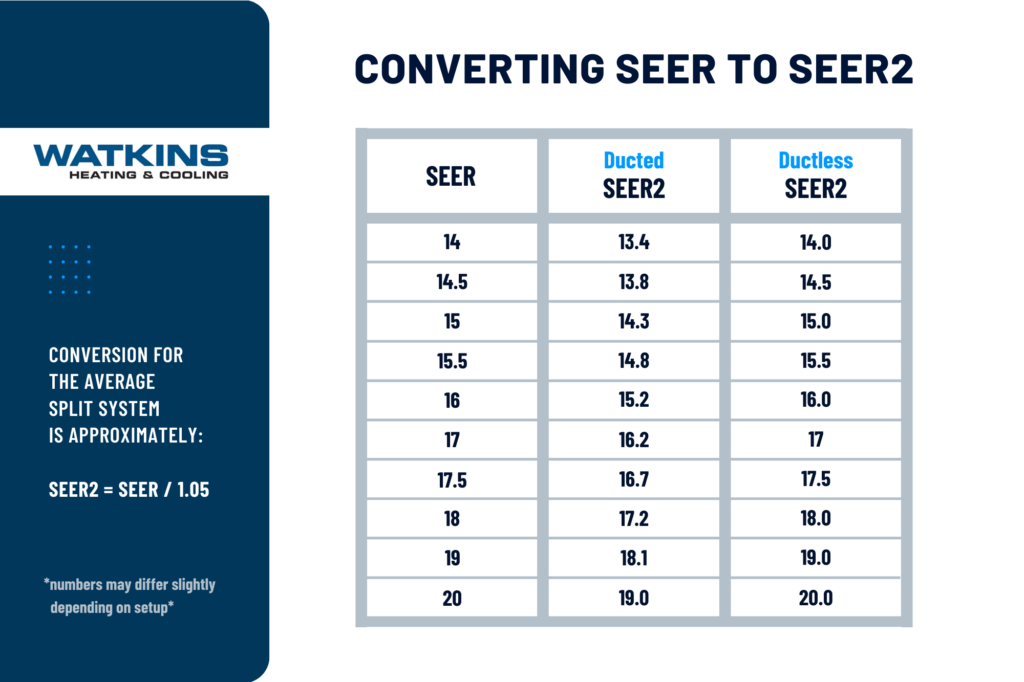
Many homeowners want to know how to convert SEER numbers to SEER2. To convert, simply divide the old SEER rating by 1.05, and you will get an estimate of what the new SEER2 rating would be. This is an approximate number, but will give you a close idea of the conversion for most systems.
The SEER2 rating reflects stricter testing conditions, which means the same system will usually have a slightly lower efficiency rating under the new standard.
Think of it like taking two different IQ tests: the new test is harder than the old one. Your score on the new test will likely be lower, but that doesn’t mean your intelligence (or in this case, your system’s efficiency) has changed. It’s just a more thorough test.
For example, an air conditioner with a 16 SEER rating under the old standard might now have a SEER2 rating closer to 15.2. This difference highlights how the system performs with factors like realistic static pressures and ductwork resistance.
To help make this change easier, we’ve created the SEER to SEER 2 Conversion Chart below. It offers a quick comparison of SEER to SEER2 ratings, so you can see how older models would score with the new standards. While there may be slight variations based on system setup, this chart serves as a helpful guide to navigate the changes:
What is the Difference Between SEER and SEER2?
The key difference between SEER and SEER2 is an upgrade in how the HVAC equipment is tested. SEER2 testing better accounts for conditions like external static pressure which were not properly considered in the old SEER testing. SEER2’s standards are overall more thorough and strive to recreate real-world elements as closely as possible.
Today’s air conditioner and heat pump ratings now better reflect what you’ll actually experience with them in your home and what you can expect in energy savings.
While the improvement in testing is the only real change from SEER to SEER2, you will notice that the new testing also led to a slightly different number for each unit. We’ll explain that difference in the next section!
Is SEER2 Better Than SEER?
SEER2’s high standards do give us a more accurate measure of a cooling system’s efficiency than SEER did. However, HVAC systems with a SEER2 rating are NOT automatically better or more efficient than systems with the old SEER rating, they are simply being tested in a new way.
Most manufacturers simply took existing air conditioners and heat pumps, re-tested them, then changed the model number to reflect the new SEER2 rating. For example, the 2022 Trane XL16i achieved 16.0 SEER in most sizes. Under the new testing, the same central air conditioning unit hits about 15.2 SEER2, so Trane simply changed the model name to XL15i. The actual cooling efficiency of this unit did NOT change, the rating was just measured differently.
How Do You Calculate Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio?
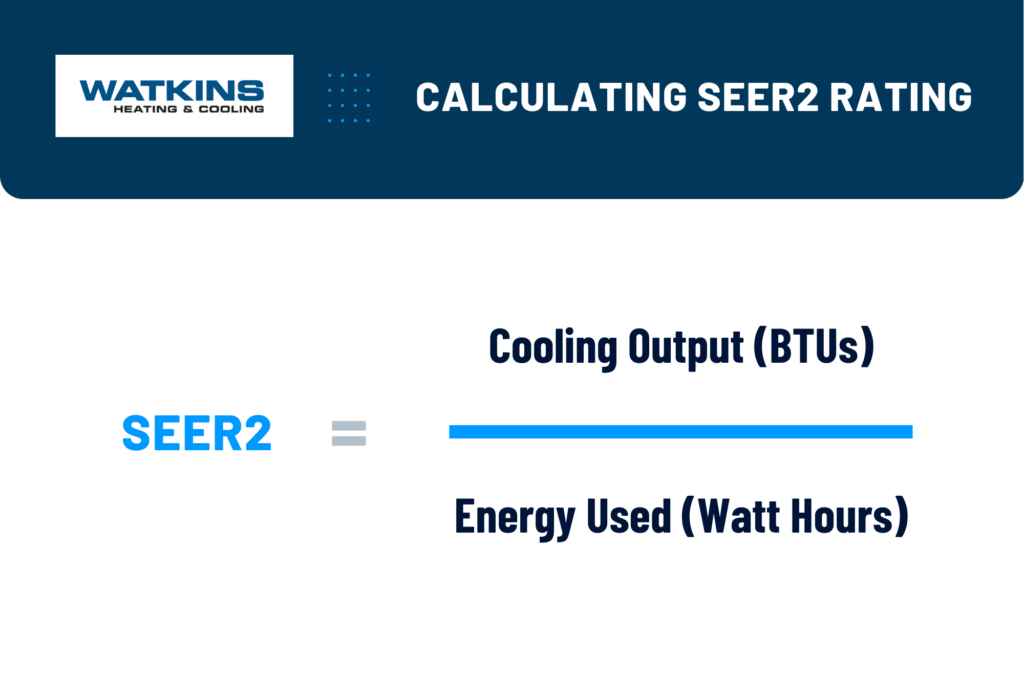
How we arrive at the actual SEER2 number is a fairly easy equation. First, we take the total cooling output of an air conditioner in a typical cooling season in the United States (measured in BTUs). Then we divide that by the total amount of electricity used during that time (measured in Watt-Hours). The higher the number, the more energy efficient the air conditioning system is.
What are EER2 and HSPF2?
We aren’t going to delve into these two terms much in this article, but both EER2 and HSPF2 are very similar to SEER2.
EER stands for Energy Efficiency Ratio and is nearly the same thing as SEER, except that it only provides a snapshot of a system’s efficiency at a very specific temperature and humidity. The EER2 rating is calculated the same as SEER2, just at a fixed indoor and outdoor temperature instead of measuring across a broad range. SEER2 measures a system’s performance over the entire cooling season, so EER2 is a less complete picture. But EER2 can be helpful for telling you how the system will perform on a specific day – for instance, 95°F outdoor temperature and 85℉ indoor temperature.
HSPF stands for Heating Seasonal Performance Factor and is very similar to SEER, but it specifically measures the efficiency of heat pumps during the heating season. SEER2 can tell us how heat pumps perform during the cooling season of spring and summer, while HSPF2 tells us the heat pump’s energy efficiency during the heating months of fall and winter.
What is the Minimum SEER2 Rating for 2025?
The SEER2 rating came out toward the end of 2022, and as of January 1, 2023, SEER2 became the new DOE efficiency standard.
All air conditioners and heat pumps manufactured today are required to be certified to the new SEER2 regulations, so HVAC manufacturers had to discontinue or redesign their lower-efficiency base models to meet the new minimum standards.
For you as a homeowner, this is one of the best things about the whole SEER system. It sets a baseline efficiency that every HVAC system must meet, so you can be confident that the new AC you’re getting is sufficiently energy efficient.
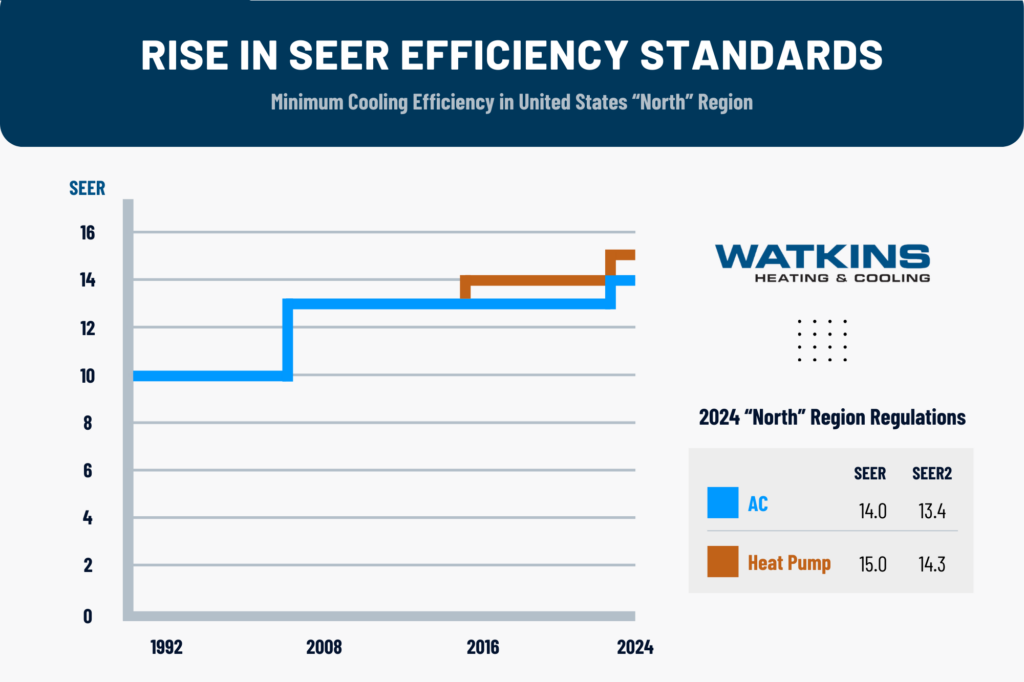
The 2025 minimum standard for air conditioners in Ohio is 13.4 SEER2 (equivalent to the 14 SEER in the old rating system). For Ohio heat pumps, the new minimum is 14.3 SEER2 and 7.5 HSPF2 (equivalent to 15 SEER and 8.8 HSPF). Manufacturers cannot legally sell anything below this.
The typical number range you’ll see for modern air conditioners is a SEER2 rating between 13 and 21. The brand Trane, for instance, offers AC and heat pump systems ranging from 13.4 SEER2 up to 21.5 SEER2.
SEER2 Regional Regulations
Where you live is key when it comes to energy efficiency regulations.
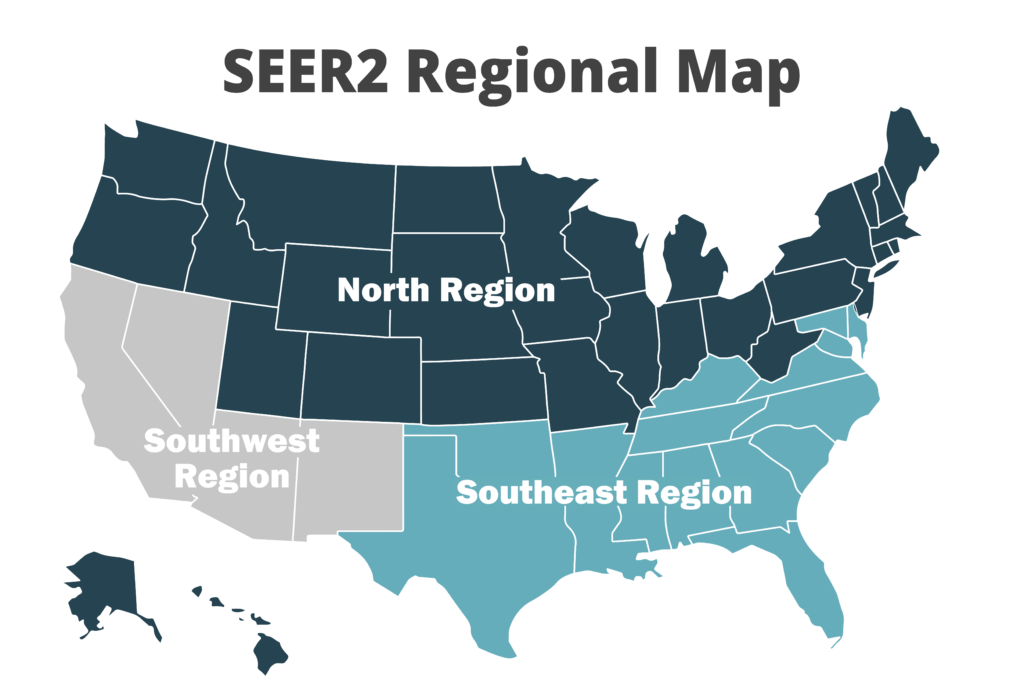
The DOE realizes that high-efficiency cooling is most important in hot climates, so in their latest regulations, they divided the U.S. into three regions. Each of these regions has its own minimum efficiency ratings based on the varying climates. The Southeast and Southwest, for example, have higher requirements for air conditioners since they’re warmer climates, while the North region requires better heat pumps to earn tax credits.
This system of regulation by region makes a lot of sense, but it has also created costly compliance rules and inventory issues for HVAC distributors.
For instance, Cincinnati HVAC suppliers carry 13.4 SEER2 air conditioners for sale in Ohio, which is part of the North Region. However, those air conditioners cannot be sold to their customers in Kentucky because it is in the Southeast region, where the minimum efficiency for ACs is 14.3 SEER2. Also, mid-grade split system heat pumps earn a federal tax credit in Kentucky, but just across the river in Ohio, homeowners must use the more expensive “cold-climate heat pump” to qualify for the same tax credit.
What SEER Rating Do I Need for a Tax Credit in 2025?
To encourage the push toward energy efficiency, the government gives money back in the form of a tax credit if you purchase some of the most highly efficient air conditioning systems.
This HVAC tax credit is provided under part 25C in the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and is available for ten years starting in tax year 2025. Under the new 2025 guidelines, the requirement for air conditioners to get the tax credit is at least 16.0 SEER2 (and 12.0 EER2). If you purchase an air conditioner that meets these efficiency standards, you’re eligible for $600, or up to $1,200 if you pair it with a qualifying gas furnace.
The tax credit for heat pumps varies based on where you live. In Ohio, heat pumps must qualify as an “Energy Star Cold Climate Heat Pump.” To achieve this rating and get the tax credit, heat pumps must first be at least 15.2 SEER2 and 8.1 HSPF2. In addition, the heat pump must maintain a very high heat output even at low temperatures. To achieve this rating generally requires an inverter-driven compressor such as the Trane XV18 or XV20i.
In all cases, you will need a certificate from the AHRI. This certificate verifies that your exact system match (furnace + AC + evaporator coil) achieves the minimum energy efficiency for a tax credit. Make sure your HVAC contractor shows you this document BEFORE you sign the proposal. Your CPA should ask for a copy and then keep it with your tax return in case of an audit. If you’re interested in getting a tax rebate for a new HVAC system, we recommend consulting with a tax professional or the IRS.
How Does SEER2 Affect Air Conditioner Costs?
If you’ve gotten a quote lately, the price increase may seem like more than normal inflation, and that’s partially true. SEER2 did not directly change the actual technology or price of air conditioners, but it did force HVAC manufacturers to recalculate the energy efficiency of all existing models and print new energy guide labels. The compliance with this new set of regulations has been a paperwork and regulation nightmare for the entire HVAC industry. Unfortunately, that regulatory cost is being passed on to the consumer with higher SEER2 prices.
Furthermore, as of January 1, 2023, no central air conditioner or heat pump can be produced if it does not meet the SEER2 requirements. Many of the cheaper, less-efficient systems were banned, and homeowners now have no choice but to buy the more efficient, more expensive models.
It can be confusing when you see that the price of a 2025 15 SEER2 air conditioner is higher than a 2022 15 SEER air conditioner, but remember that the 15 SEER2 is more efficient than the 15 SEER. For a more accurate comparison, look at the difference between today’s 15 SEER2 model and a 2022 16 SEER.
Choosing Your Air Conditioner
The move to SEER2 comes with a lot of positives. It gives homeowners like you a more accurate picture of how your AC system will perform, and it helps us all move toward a new era of energy efficiency.
However, homeowners should be aware that many HVAC contractors are still using using old SEER numbers or old model names to misrepresent the efficiency of their product.
At Watkins Heating & Cooling, transparency is who we are, and we will always share the latest ratings with you for the most accurate, up-to-date understanding of your system’s efficiency.
If you’re shopping for a new air conditioner, check out our Air Conditioner Pricing page here.
If you still have questions about energy efficiency or you’re looking for a new heating and cooling system, we would love to walk you through all of our different options or send out a qualified technician to determine the perfect fit for your needs.
Reach out to our honest, helpful HVAC team at Watkins Heating & Cooling below. We’re always here for you.